The Riparian Condition Assessment (RCA) tool models the condition of riparian areas based on three inputs: riparian vegetation departure (as modeled using the RVD tool), land use intensity, and floodplain connectivity. Each segment of an input network is attributed with values on continuous scales for each of these three inputs. The output (condition) of each segment is then assessed using a fuzzy inference system. The tool produces an output polyline shapefile which includes the three model inputs as attributes, as well as an output table that contains the calculated condition for each segment which can be joined to the polyline using the “FID” field.
Step 1: Run the RCA Project Builder tool.
This tool builds the folder structure for running RCA. See here for pre-processing steps of input data.
Parameters
- Select project folder: Select newly created folder to store all RCA inputs, intermediates, and outputs in.
- Select existing cover folder: Select folder holding LANDFIRE existing vegetation data for the area of interest.
- Select historic cover folder: Select folder holding LANDFIRE historic vegetation data for the area of interest.
- Select drainage network datasets: Select pre-processed segmented network shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
- Select fragmented valley bottom datasets: Select pre-processed valley bottom shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
- Select large river polygons (optional): Select large river shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
- Select dredge tailings polygons (optional): Select dredge tailings shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
NOTE: See the RVD page for figures showing how including dredge tailings affects vegetation values.
Step 2: Run the RCA tool
This tool calculates all intermediates and outputs.
Parameters
- Project Name (optional): Project name to be used in the XML metadata file.
- Watershed HUC ID (optional): Watershed HUC ID to be used in the XML metadata file.
- Watershed Name (optional): Watershed name to be used in the XML metadata file.
- Select Project Folder: Select project folder created in the RCA Project Builder.
- Existing Cover Raster: Select the LANDFIRE EVT layer from the inputs folder within the project folder.
- Historic Cover Raster: Select the LANDFIRE BPS layer from the inputs folder within the project folder.
- Input Segmented Stream Network: Select the stream network shapefile from the inputs folder within the project folder.
NOTE: In the current version of the tool, if the stream network contains too many features (or segments), the tool will run out of memory and fail to run. Stream networks for watersheds can be clipped down to subwatersheds to run the tool with, and then the outputs can be merged together. For future versions, this issue will be resolved.
-
Input Fragmented Valley Bottom: Select the valley bottom shapefile from the inputs folder within the project folder.
- Large River Polygon (optional): Select the large river shapefile from the inputs folder. In areas with large rivers (ie Green, Colorado, Snake, Columbia), all landcover cells within these large river polygons are coded as no data. In smaller rivers, the open water landcover class is coded as riparian. In development, we found that coding open water in large rivers as riparian skewed them to appear to be in better condition than they are. In small rivers, if open water was not coded as riparian, they appeared to be in worse condition than they were. The “Area” shapefile that was downloaded with NHD data can generally be used as this large river polygon.
- Dredge Tailings Polygon (optional): Select dredge tailings shapefile from the inputs folder. In areas with dredge tailings, existing riparian landcover is coded with a vegetation score of “0” - i.e., no riparian vegetation.
- Valley Bottom Width Threshold: Enter a width value above which streams will be considered “unconfined” and below which the streams will be considered “confined.”
NOTE: the process used to calculate valley width gives a rough, over-estimated estimate, so this value should also be over-estimated (for example the default value of 190 meters for the tool is roughly 100 meters on the ground). The value can be decreased from the default value (190) in order to include more of the network as unconfined, or increased in order to include less of the network as unconfined.
- Name RCA Output: Specify name for the final polyline output which will be saved in the outputs folder within the project folder.
Outputs
- The RCA output symbolized using the default symbology of the
CONDITIONfield.
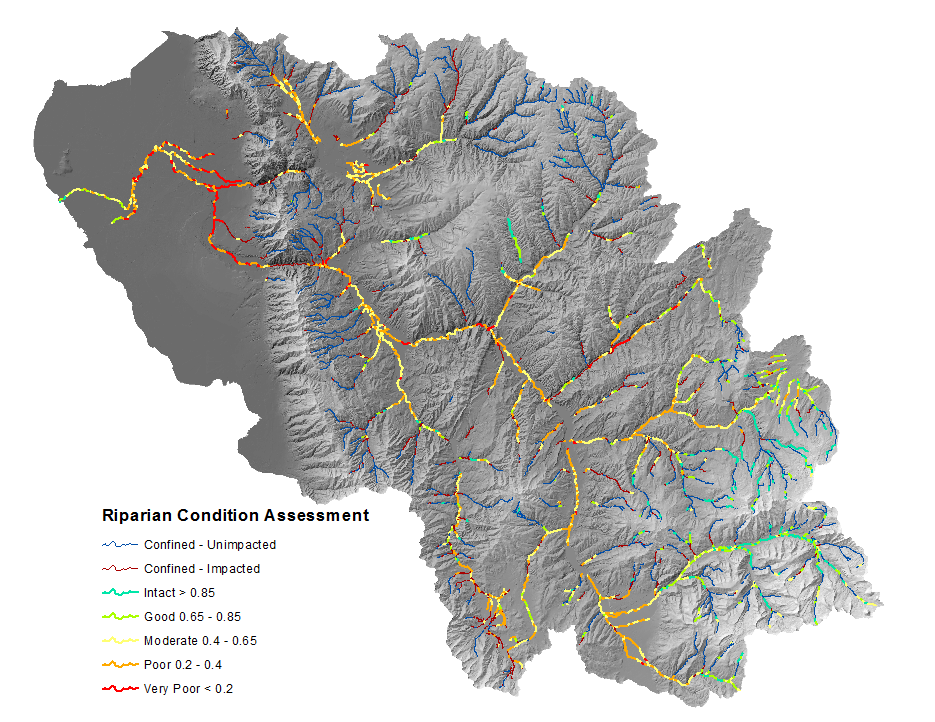
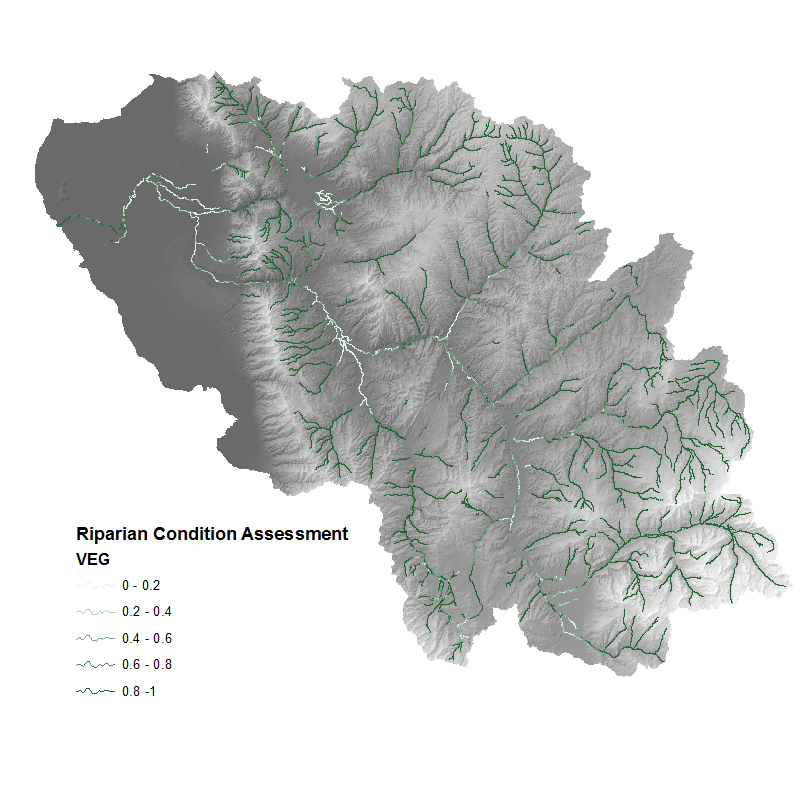
Additionally the VEG field may be of interest, and simply represents the proportion of historic vegetation cover (riparian and non-riparian) that exists on the landscape today.
- The RCA output symbolized using the
VEGfield to show the proportion of historic vegetation cover that exists now.
Additional RCA Output Fields
RVD: The riparian vegetation departure score (proportion of historic riparian vegetation) for the given stream segment. LUI: The Land Use Intensity index, on a scale from 0 (high) to 3 (low). CONNECT: The proportion of the polygon (floodplain) associated with stream segment that is accessible to the stream. COND_VAL: A value on a continuous index from 0 to 1 that represents the condition of the riparian area for unconfined streams. (a value of 0 means that the stream is confined and the value is not relevant.)
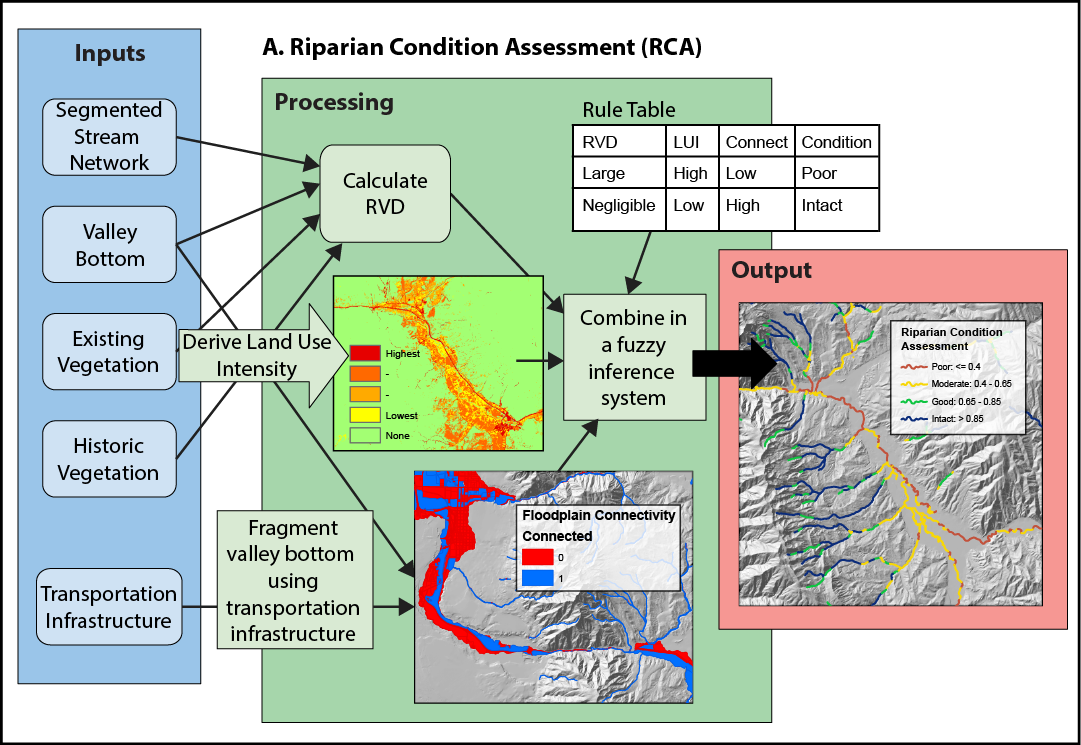
Conceptual diagram showing how riparian condition assessment is calculated