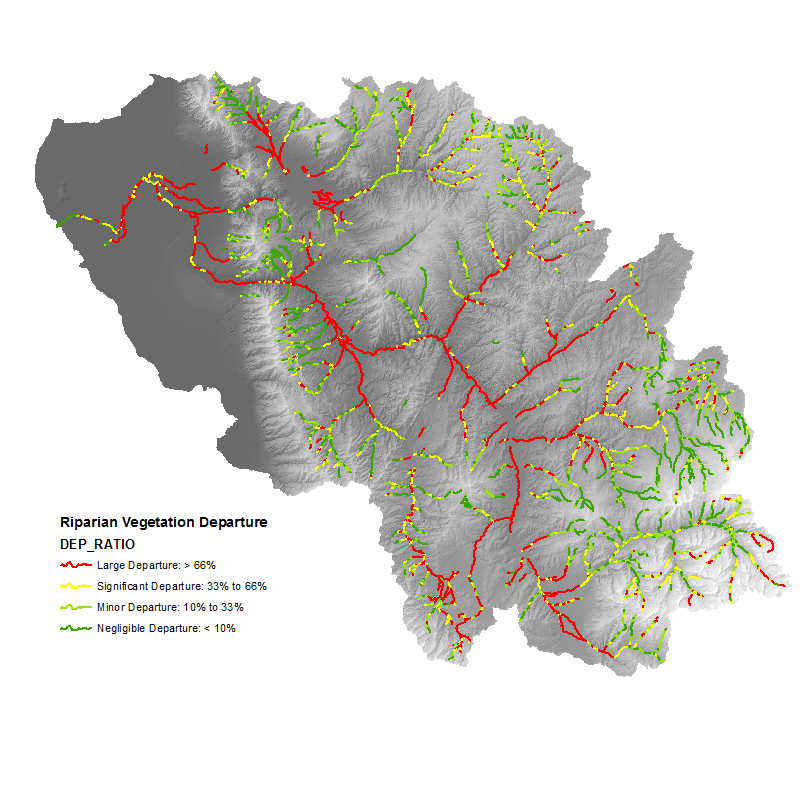
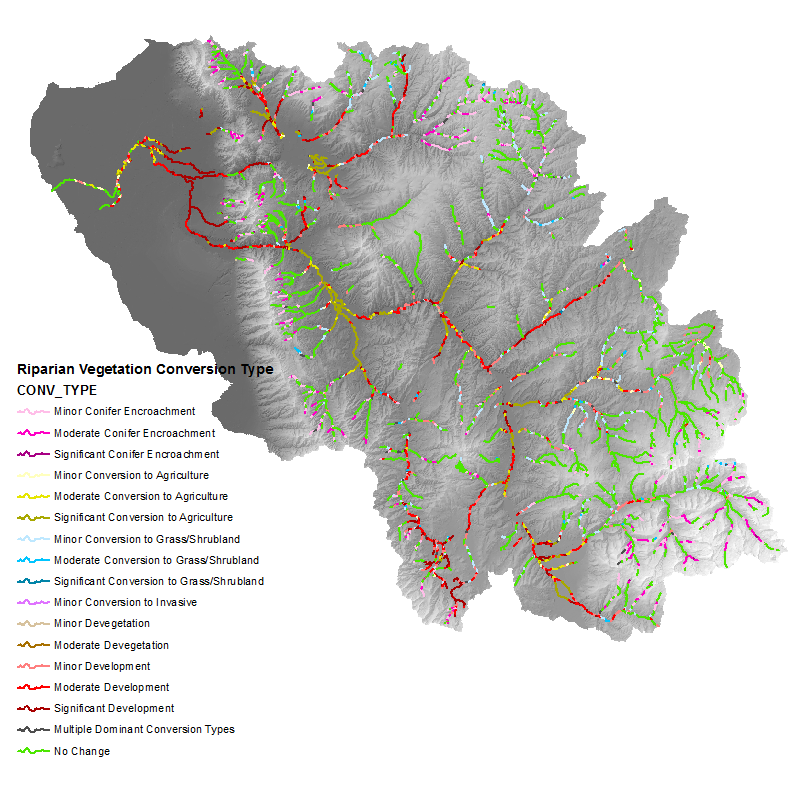
The Riparian Vegetation Departure (RVD) tool uses LANDFIRE landcover inputs to determine the departure of riparian vegetation from pre-settlement conditions. Current riparian vegetation cover is modeled using the LANDFIRE Existing Vegetation Type (EVT) layer. Historic (pre-European settlement) vegetation is modeled using the LANDFIRE Bio-physical Setting (BpS) layer. For more information on these layers see LANDFIRE’s website. In both of these layers, all native, riparian vegetation is given a value of 1, and all other vegetation is given a value of 0. The valley bottom is broken into polygons that correspond to approximately 500 meter segments of stream network, and within each polygon, the number of existing riparian cells is divided by the number of modeled historic riparian cells. The result is a ratio that represents the proportion of historic riparian vegetation that currently exists on the landscape. This value is then applied to the network. In addition, an analysis is performed that looks at types of riparian conversion and quantifies each type within each stream segment to determine possible causes of riparian degradation.
Step 1: Run the RVD Project Builder tool.
This tool builds the folder structure for running RVD. See here for pre-processing steps of input data.
Parameters
- Select Project Folder: Select newly created folder to store all RCA inputs, intermediates, and outputs in.
- Select existing vegetation folder: Select folder holding LANDFIRE existing vegetation data for the area of interest.
- Select historic vegetation folder: Select folder holding LANDFIRE historic vegetation data for the area of interest.
- Select drainage network datasets: Select pre-processed segmented network shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
- Select valley bottom datasets: Select pre-processed fragmented valley bottom shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
- Select large river polygons (optional): Select large river shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
- Select dredge tailings polygons (optional): Select dredge tailings shapefile(s) you want to use in this RCA run.
Step 2: Run the RVD tool
This tool calculates the riparian vegetation departure and conversion types outputs
Parameters
- Project Name (optional): Project name to be used in the XML metadata file.
- Watershed HUC ID (optional): Watershed HUC ID to be used in the XML metadata file.
- Watershed Name (optional): Watershed name to be used in the XML metadata file.
- Select Project Folder: Select project folder created by the RVD Project Builder.
- Existing Vegetation Raster: Select the LANDFIRE EVT layer for the area of interest.
- Historic Vegetation Raster: Select the LANDFIRE BPS layer for the area of interest.
- Input Segmented Stream Network: Select the stream network shapefile from the inputs folder within the project folder.
- Input Valley Bottom Polygon: Select the fragmented valley bottom polygon shapefile from the inputs folder within the project folder.
- Large River Polygon (optional): Select the large river polygon shapefile from the inputs folder. In areas with large rivers (ie Green, Colorado, Snake, Columbia), all landcover cells within these large river polygons are coded as no data. In smaller rivers, the open water landcover class is coded as riparian. In development, we found that coding open water in large rivers as riparian skewed them to appear to be in better condition than they are. In small rivers, if open water was not coded as riparian, they appeared to be in worse condition than they were. The “Area” shapefile that was downloaded with NHD data can generally be used as this large river polygon.
- Dredge Tailings Polygon (optional): Select the dredge tailings shapefile from the inputs folder. In areas with dredge tailings, existing riparian landcover is coded with a vegetation score of “0” - i.e., no riparian vegetation.
- Name RVD Output: Specify a name to store the final polyline output, which will be found in the outputs folder within the project folder.
Standard Outputs
- Riparian Vegetation Departure ratio
DEP_RATIO
- Riparian Vegetation Conversion Type
CONV_TYPE
Comparison of Outputs with and without Dredge Tailings Input
- Riparian Vegetation Departure ratio without adjustment for dredge tailings
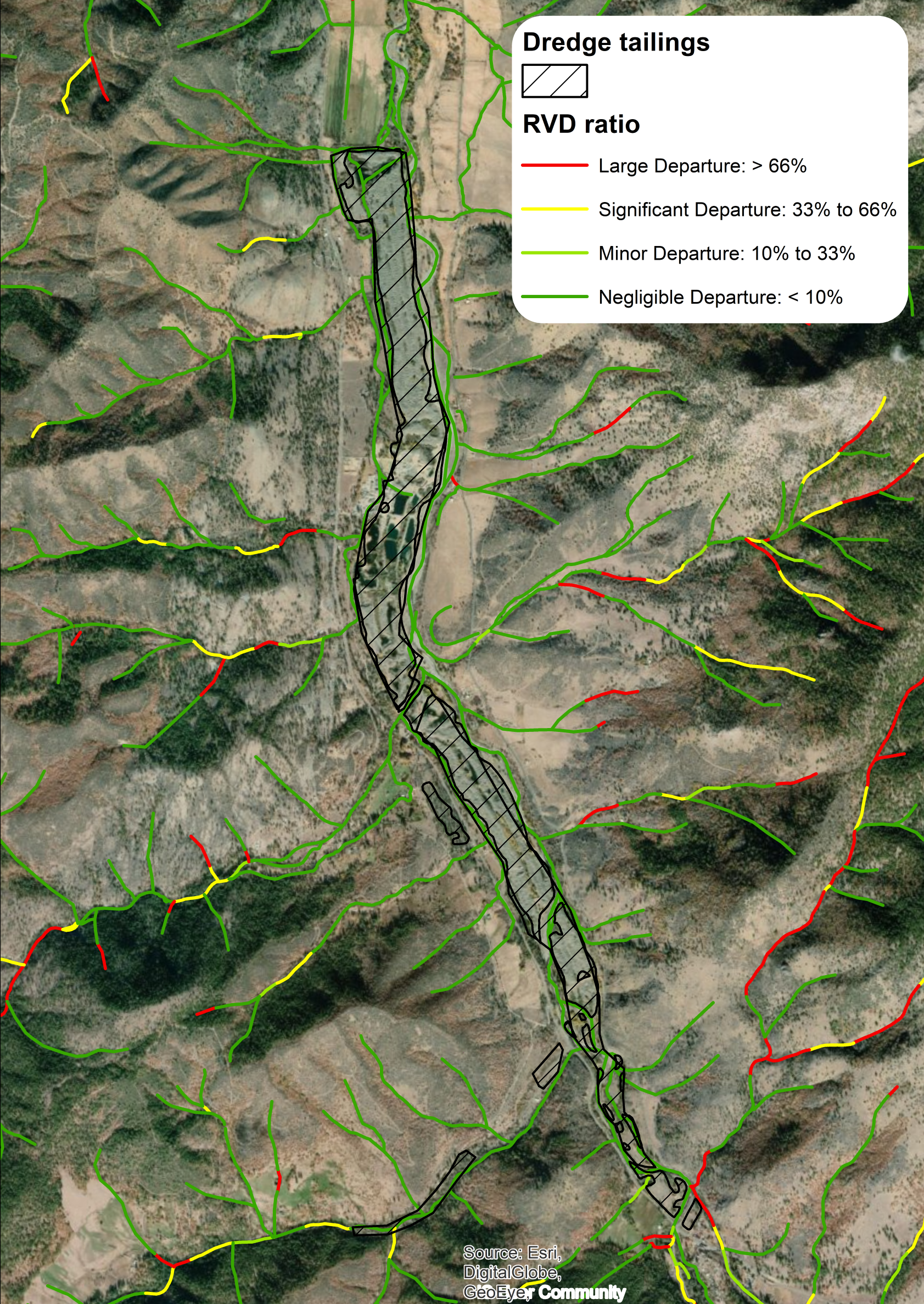
- Riparian Vegetation Departure ratio with adjustment for dredge tailings
Additional RVD Output Fields
EVT_MEAN: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment with existing riparian cover. BPS_MEAN: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment with historic riparian cover. COUNT: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment that were historically riparian. sum_noch: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment whose conversion type is ‘no change.’ sum_grsh: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment whose conversion type is ‘conversion to grass/shrubland.’ sum_deveg: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment whose coversion type is ‘devegetate.’ sum_con: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment whose conversion type is ‘conifer encroachment.’ sum_inv: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment whose conversion type is ‘coversion to invasive.’ sum_dev: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment whose conversion type is ‘developed.’ sum_ag: the number of cells within the polygon corresponding to stream segment whose conversion type is ‘conversion to agriculture.’ prop_noch: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment where riparian remained riparian (sum_noch/COUNT). prop_grsh: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment in which riparian was converted to grassland or shrubland(sum_grsh/COUNT). prop_deveg: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment in which riparian was removed and no vegetation took it’s place (ie remained dirt or rock) (sum_deveg/COUNT). prop_con: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment in which riparian was converted to conifer forest (sum_con/COUNT). prop_inv: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment in which riparian was converted to invasive vegetation (sum_inv/COUNT). prop_dev: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment in which riparian was converted to developed areas (sum_dev/COUNT). prop_ag: proportion of polygon corresponding to stream segment in which riparian was converted to agriculture (sum_ag/COUNT).
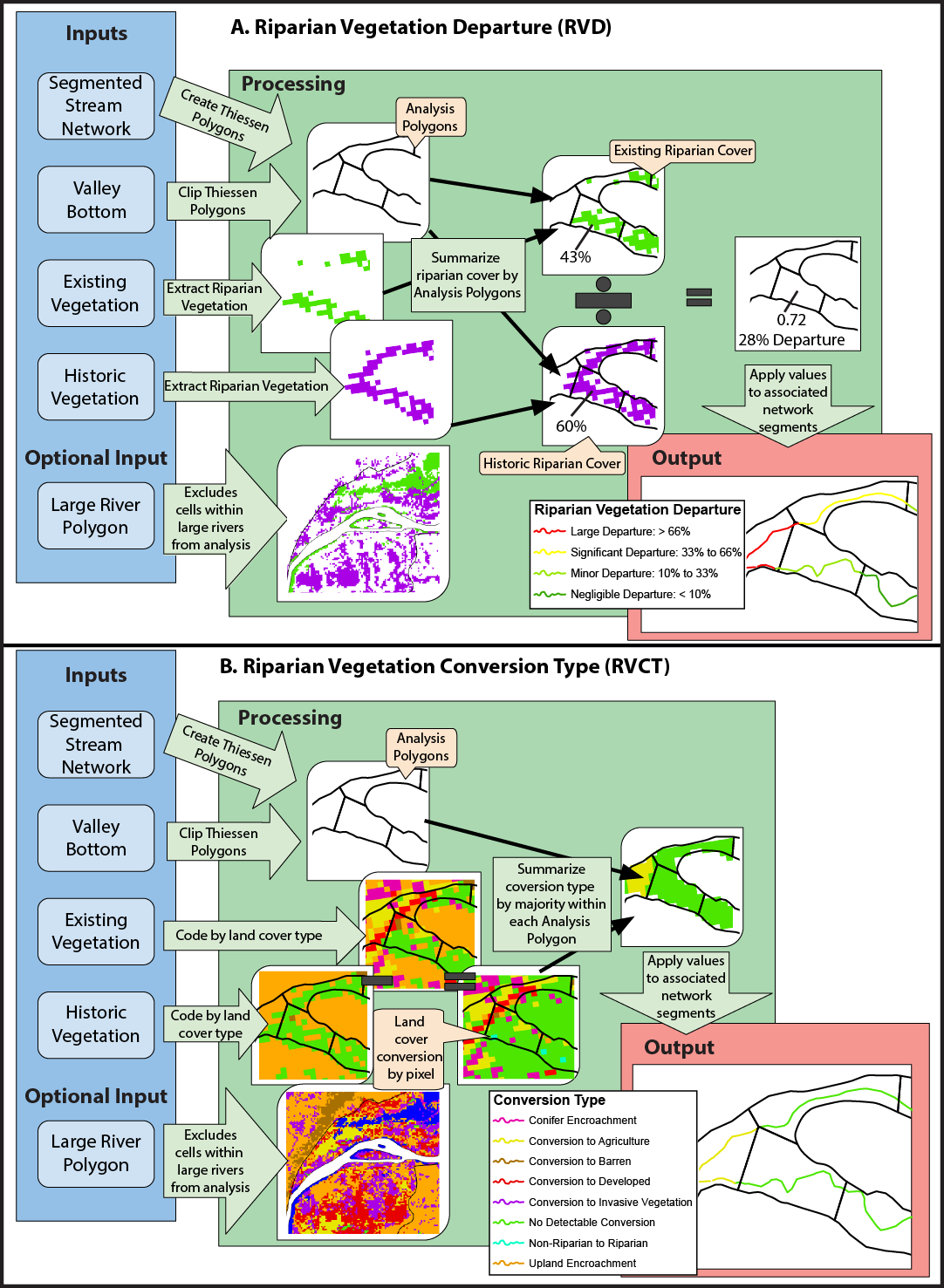
Conceptual diagram showing how vegetation departure from historic and riparian vegetation conversion type are calculated